Basic Rules of BIM MEP coordination:
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has revolutionized the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry by enhancing collaboration, improving accuracy, and streamlining project management. Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) coordination is a critical aspect of BIM, ensuring that all systems work harmoniously within a building. Effective MEP coordination can prevent costly clashes, reduce rework, and improve overall project efficiency.
Here are some basic rules and best practices to follow for successful BIM MEP coordination.

1. Early Involvement of All Stakeholders
Early involvement of all project stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and owners, is crucial. This ensures that everyone’s requirements and constraints are understood and integrated into the design from the beginning, reducing the likelihood of conflicts later on.
2. Establish Clear Communication Channels
Clear and consistent communication is vital for effective MEP coordination. Regular meetings, updates, and a centralized communication platform help keep everyone informed and aligned. Use collaborative tools within the BIM environment to share updates and resolve issues promptly.
3. Define Coordination Zones
Dividing the building into coordination zones helps manage the complexity of MEP systems. Each zone can be coordinated independently before integrating them into the overall model. This approach simplifies the process and allows for more focused attention on specific areas.
4. Standardize Clash Detection Procedures
Utilize clash detection tools within BIM software to identify and resolve conflicts between MEP systems and other building components. Establish a standardized procedure for clash detection, including regular clash detection runs, reporting protocols, and a systematic approach to resolving identified clashes.
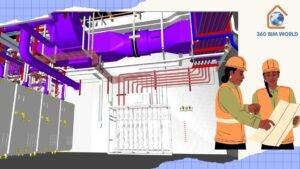
5. Adopt a Common Data Environment (CDE)
A Common Data Environment (CDE) is essential for maintaining a single source of truth for all project data. This centralized repository ensures that everyone is working with the latest information, reducing the risk of errors and miscommunication. Ensure that all stakeholders have access to the CDE and understand how to use it effectively.
6. Follow Industry Standards and Best Practices
Adhere to industry standards and best practices for MEP coordination, such as those outlined by the National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS), American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE), and other relevant organizations. These standards provide guidelines for efficient and effective MEP coordination.
7. Implement Regular Quality Control Checks
Regular quality control checks ensure that the MEP models meet the required standards and specifications. This includes checking for compliance with design criteria, verifying the accuracy of model data, and ensuring that all systems are properly coordinated.
8. Leverage 3D Visualization
3D visualization tools within BIM software help stakeholders understand the spatial relationships between different MEP systems and other building components. Use these tools to conduct virtual walkthroughs, identify potential issues, and communicate design intent clearly.
9. Prioritize Space Allocation for MEP Systems
Early space allocation for MEP systems helps avoid conflicts and ensures that sufficient space is available for installation and maintenance. Coordinate with architects and structural engineers to reserve adequate space for ducts, pipes, and other MEP components.
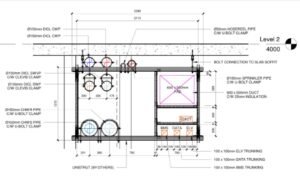
10. Plan for Future Maintenance and Access
Design MEP systems with future maintenance and access in mind. Ensure that there is sufficient clearance for maintenance personnel and equipment, and that critical components are easily accessible. This foresight can save time and costs in the long run.
11. Utilize Space Management Systems
Space management systems within BIM tools are essential for optimizing the use of available space and ensuring that all MEP systems are properly coordinated. These systems help in identifying potential space conflicts, managing spatial requirements, and ensuring that the design adheres to building codes and standards. Effective space management can lead to more efficient layouts, easier maintenance, and reduced construction costs. Implementing a robust space management strategy can significantly enhance the coordination process and overall project outcomes.
FAQ
Q1: What is BIM MEP coordination?
BIM MEP coordination involves using Building Information Modeling (BIM) to ensure that mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems are properly integrated and work harmoniously within a building’s design. This process helps prevent clashes, reduces rework, and enhances project efficiency.
Q2: Why is early involvement of stakeholders important in MEP coordination?
Early involvement ensures that all stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and owners, can communicate their requirements and constraints from the start. This reduces the likelihood of conflicts and helps integrate all necessary considerations into the design early on.
Q3: How do clash detection tools work in BIM?
Clash detection tools within BIM software identify conflicts between different building components, such as MEP systems and structural elements. These tools highlight areas where components overlap or interfere with each other, allowing for adjustments to be made before construction begins.
Q4: What is a Common Data Environment (CDE) and why is it important?
A Common Data Environment (CDE) is a centralized repository for all project data. It ensures that all stakeholders have access to the latest information, reducing the risk of errors and miscommunication. The CDE serves as the single source of truth for the project.
Q5: How can 3D visualization aid in MEP coordination?
3D visualization tools help stakeholders understand the spatial relationships between different MEP systems and other building components. They enable virtual walkthroughs, making it easier to identify potential issues, communicate design intent, and enhance overall project understanding.
Q6: What role does space management play in MEP coordination?
Space management systems help optimize the use of available space, ensuring that all MEP systems are properly coordinated. These systems identify potential space conflicts, manage spatial requirements, and ensure adherence to building codes and standards, leading to more efficient layouts and reduced construction costs.
Conclusion
Effective BIM MEP coordination is essential for the success of any construction project. By following these basic rules and best practices, including the implementation of space management systems, you can ensure that your MEP systems are well-coordinated, reducing the risk of conflicts, improving project efficiency, and delivering a better final product. Embrace the power of BIM to enhance collaboration, accuracy, and project outcomes in the AEC industry.
