Mastering BIM Dimensions:
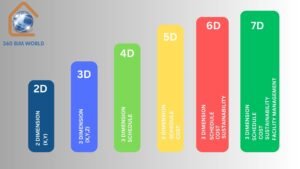
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry by enhancing collaboration, reducing errors, and improving project outcomes. One key aspect of BIM that professionals need to understand is the concept of BIM dimensions. These dimensions extend beyond the traditional 3D modeling to include additional data that can significantly impact project management and delivery. In this guide, we will explore the different BIM dimensions: 3D, 4D, 5D, 6D, and 7D BIM.
BIM is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility. It serves as a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility, forming a reliable basis for decisions during its lifecycle from inception onward. The dimensions of BIM extend this concept, integrating various types of data to enhance project insights and decision-making processes.
3D BIM: The Foundation
3D BIM involves creating a three-dimensional digital model of a building. This model includes detailed geometrical and graphical representations of the structure. The primary benefits of 3D BIM include improved visualization, enhanced design accuracy, and the ability to detect clashes early in the design phase. By using 3D BIM, stakeholders can better understand the spatial relationships and aesthetics of the project, leading to more informed decisions.
4D BIM: Time Management
4D BIM adds the element of time to the 3D model. This dimension involves integrating the construction schedule with the 3D model, enabling project managers to visualize the construction sequence over time. With 4D BIM, stakeholders can simulate the entire construction process, identify potential delays, and optimize the construction timeline. This leads to better project planning, more efficient scheduling, and reduced risk of project overruns.
5D BIM: Cost Estimation
5D BIM incorporates cost data into the 3D model. This dimension allows for accurate cost estimation and budget management throughout the project lifecycle. By linking cost information with the 3D model, project teams can generate real-time cost forecasts, track budget variances, and make more informed financial decisions. 5D BIM helps in controlling costs, improving financial predictability, and ensuring the project stays within budget.
6D BIM: Sustainability and Facility Management
6D BIM focuses on the sustainability and operational aspects of the building. This dimension includes data related to energy consumption, sustainability measures, and facility management. By integrating this information into the BIM model, stakeholders can analyze the environmental impact, optimize energy performance, and plan for efficient facility maintenance. 6D BIM supports the creation of sustainable buildings and enhances long-term operational efficiency.
7D BIM: Lifecycle Management
7D BIM involves managing the entire lifecycle of a building, from design and construction to operation and maintenance. This dimension includes comprehensive data about the building’s components, maintenance schedules, and lifecycle costs. By using 7D BIM, facility managers can ensure that the building operates efficiently, maintenance is performed proactively, and overall lifecycle costs are minimized. This dimension is crucial for extending the longevity and performance of the building.

Conclusion
Understanding the different dimensions of BIM is essential for maximizing the benefits of this powerful technology. From improved visualization and time management to accurate cost estimation and sustainable building practices, BIM dimensions provide a comprehensive framework for managing complex construction projects. By embracing 3D, 4D, 5D, 6D, and 7D BIM, professionals in the AEC industry can achieve better project outcomes, enhance collaboration, and drive innovation.
FAQs about BIM Dimensions
Q1: What is BIM? A: Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility. It serves as a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility, forming a reliable basis for decisions during its lifecycle from inception onward.
Q2: What are the different BIM dimensions? A: The different BIM dimensions are:
- 3D BIM: Three-dimensional modeling.
- 4D BIM: Time and scheduling data.
- 5D BIM: Cost estimation data.
- 6D BIM: Sustainability and facility management data.
- 7D BIM: Lifecycle management data.
Q3: What is the main benefit of 3D BIM? A: The main benefits of 3D BIM include improved visualization, enhanced design accuracy, and the ability to detect clashes early in the design phase. This leads to better spatial understanding and more informed decision-making.
Q4: How does 4D BIM improve construction project management? A: 4D BIM improves construction project management by integrating the construction schedule with the 3D model. This allows project managers to visualize the construction sequence over time, identify potential delays, and optimize the construction timeline, leading to more efficient scheduling and reduced risk of project overruns.
Q5: What role does 5D BIM play in cost management? A: 5D BIM incorporates cost data into the 3D model, allowing for accurate cost estimation and budget management throughout the project lifecycle. It helps in generating real-time cost forecasts, tracking budget variances, and making informed financial decisions, ensuring the project stays within budget.
Q6: How does 6D BIM contribute to sustainability? A: 6D BIM focuses on sustainability by integrating data related to energy consumption, sustainability measures, and facility management into the BIM model. This allows stakeholders to analyze the environmental impact, optimize energy performance, and plan for efficient facility maintenance, supporting the creation of sustainable buildings.
Q7: What is the importance of 7D BIM in lifecycle management? A: 7D BIM involves managing the entire lifecycle of a building, from design and construction to operation and maintenance. It includes comprehensive data about the building’s components, maintenance schedules, and lifecycle costs. This dimension ensures efficient operation, proactive maintenance, and minimized lifecycle costs, extending the building’s longevity and performance.
Q8: How can BIM dimensions improve collaboration in the AEC industry? A: BIM dimensions enhance collaboration by providing a comprehensive and integrated framework for project data. This enables better communication and coordination among stakeholders, reduces errors, and improves project outcomes. By using BIM dimensions, teams can work more effectively together, leading to higher efficiency and better project delivery.
Q9: Are there any challenges in implementing BIM dimensions? A: While BIM dimensions offer significant benefits, their implementation can pose challenges such as the need for specialized software, training, and changes in traditional workflows. Additionally, collaboration and data sharing across different teams and systems can be complex. However, with proper planning and investment in technology and training, these challenges can be overcome.
Q10: What software is commonly used for BIM? A: Commonly used BIM software includes Autodesk Revit, Navisworks, Bentley Systems, ArchiCAD, and Tekla Structures. These tools offer various features for 3D modeling, scheduling, cost estimation, and more, supporting the different BIM dimensions.

Pingback: "How BIM Transforms Green Building Design: Sustainable Solutions for 2024"