The Imperative of Chips: Why India’s Future is Silicon-Powered
In our increasingly interconnected world, semiconductors – the tiny chips that power everything from smartphones and AI servers to electric vehicles – are the bedrock of the digital economy. For years, India, a global powerhouse in IT services and chip design, remained largely dependent on imports, bringing in over 90% of its semiconductor needs. This reliance exposed vulnerabilities, especially during global supply chain disruptions.
Recognizing this critical strategic and economic imperative, India launched the ambitious India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) in 2021. More than just an industrial policy, the ISM is a bold national endeavor to establish a robust domestic semiconductor ecosystem, transforming India from a consumer of digital technology into a formidable manufacturing and innovation leader. This strategic pivot is central to India’s vision of achieving a $1 trillion digital economy by 2030.
The India Semiconductor Mission: A Framework for Growth
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM), backed by a substantial financial outlay of ₹76,000 crore (over $10 billion), is designed to incentivize and attract global and domestic players across the entire semiconductor value chain. Its core objectives include:
- Establishing Fab Units: Facilitating the setup of advanced semiconductor fabs in India (fabrication plants) to produce wafers.
- Boosting ATMP Capabilities: Promoting ATMP India (Assembly, Testing, Marking, and Packaging) units, a crucial step in preparing chips for end-use.
- Fostering Design & R&D: Cultivating a vibrant chip design India and research and development ecosystem.
- Talent Development: Building a highly skilled workforce in microelectronics and nanotechnology.
- Positioning India as a Global Hub: Elevating India’s stature as a trusted and resilient global semiconductor supply chain partner.
From Aspirations to Ground Reality: Major Milestones
While building a complex semiconductor industry from scratch presents significant challenges, the ISM has already spurred remarkable progress. Key projects are now underway, demonstrating India’s semiconductor mission’s commitment and growing appeal:
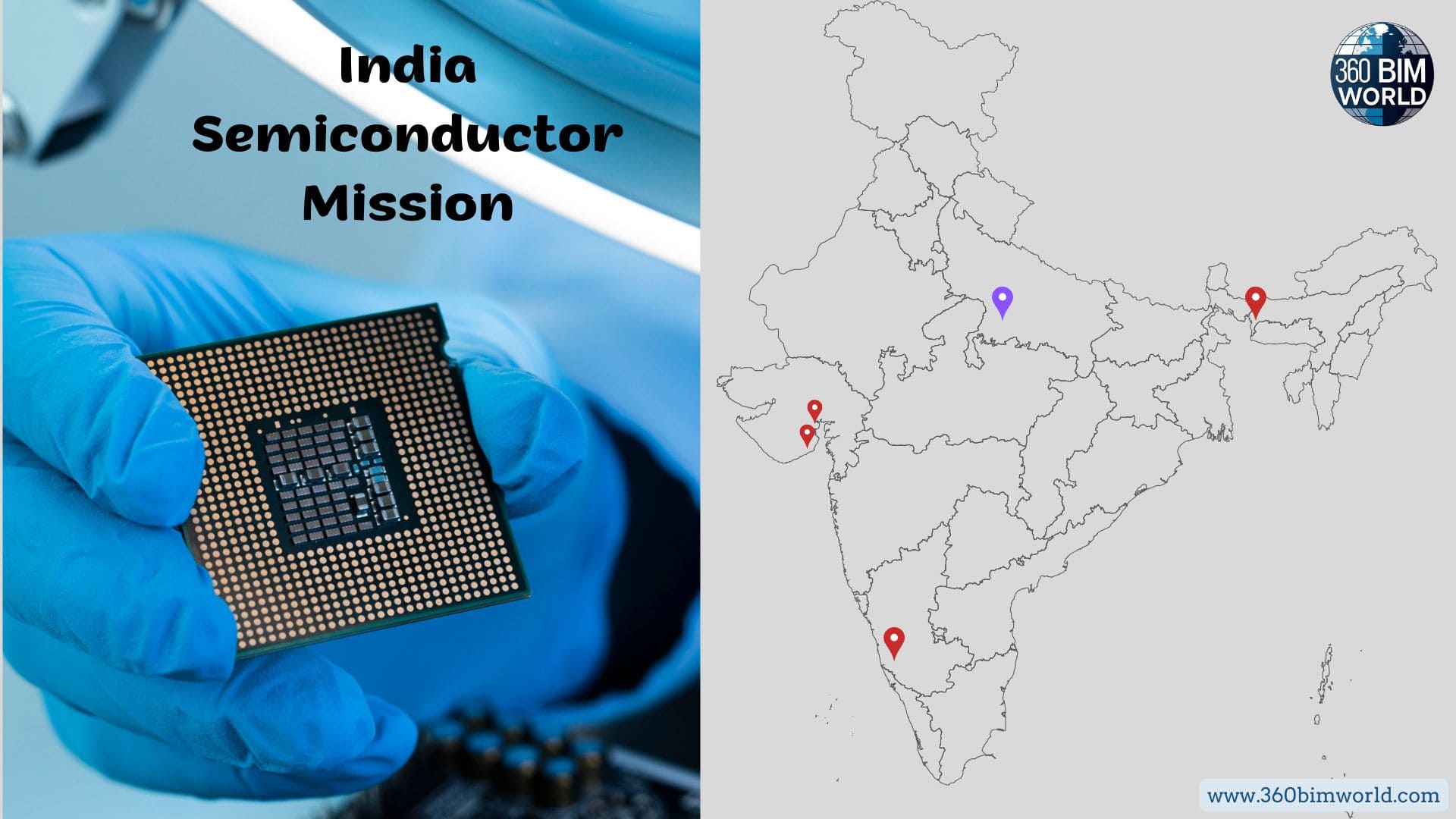
- Tata-Powerchip Fab in Dholera, Gujarat: A landmark project, Tata Group, in collaboration with Taiwan’s Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation (PSMC), is setting up India’s first indigenous chip fabrication plant in Dholera. This multi-billion dollar investment will focus on producing various chips for critical sectors like automotive, computing, and AI, with initial production anticipated by late 2026. This fab signifies a massive leap towards Make in India chips.
- Tata ATMP Plant in Jagiroad, Assam: Further solidifying its commitment, Tata Semiconductor Assembly and Test Pvt Ltd (TSAT) is building a greenfield semiconductor assembly and test facility in Jagiroad, Assam. This project, with an investment of ₹27,000 crore (around $3.25 billion), will focus on advanced packaging technologies like wire bond, flip chip, and Integrated Systems Packaging (ISP). It’s expected to be operational by mid-2025 and produce up to 48 million chips per day, generating significant direct and indirect jobs.
- Micron Technology in Sanand, Gujarat: US memory giant Micron Technology is investing $2.75 billion in a state-of-the-art semiconductor assembly and test facility in Sanand, Gujarat. This facility will handle both DRAM and NAND products, with initial operations slated for Mid of 2025, further diversifying India’s ATMP landscape.
- ISMC in Karnataka: The International Semiconductor Consortium (ISMC), a joint venture, is also progressing with plans for a significant chip manufacturing plant in Mysuru, Karnataka.
- HCL-Foxconn ATMP: As of May 2025, a joint venture between HCL and Foxconn was approved to set up another semiconductor outsourced assembly and testing unit, further diversifying India’s manufacturing capabilities.
These projects are bolstered by robust government support, including fiscal incentives, infrastructure development, and strategic land allocation, creating a conducive environment for global investments in chip manufacturing India.

Beyond Economics: The Strategic Significance
The drive for semiconductor self-reliance extends far beyond economic growth. It is a critical component of national security, economic resilience, and digital sovereignty. Recent global chip shortages underscored the vulnerability of highly concentrated supply chains. India’s emergence as a manufacturing hub directly addresses these concerns.
Furthermore, India’s geopolitically neutral stance and its commitment to robust intellectual property rights make it an attractive alternative in the context of global “China+1” diversification strategies. By providing a stable and reliable base for semiconductor production, India is poised to become a vital pillar in the evolving global semiconductor supply chain.
India’s Unparalleled Human Capital: Fueling Innovation
One of India’s most significant advantages in this mission is its vast pool of engineering talent. Producing over 1.5 million engineers annually, India already boasts a strong foundation in chip design. Global tech giants like Intel, Qualcomm, AMD, and Nvidia have long leveraged India’s expertise, operating their largest offshore R&D centers in the country.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) actively supports talent development through programs like the Design Linked Incentive (DLI) scheme and collaborations with academia. These initiatives are crucial for nurturing the next generation of engineers specializing in VLSI design, embedded systems, and cutting-edge AI hardware, ensuring India remains at the forefront of semiconductor innovation.
The Trillion-Dollar Multiplier: Economic Impact
A flourishing silicon economy will have a transformative ripple effect across numerous sectors of the Indian economy:
- Automotive: Powering the rapid expansion of electric and autonomous vehicles.
- Telecommunications: Enabling the rollout of advanced 5G and future 6G technologies.
- Defense & Aerospace: Strengthening indigenous capabilities and reducing reliance on foreign components.
- Consumer Electronics & IoT: Driving innovation in smart devices and connected ecosystems.
Projections from industry reports indicate that India’s semiconductor market is set to exceed $80 billion by 2028, with some estimates putting it over $100 billion by 2030. This exponential growth will directly contribute to India’s ambitious $1 trillion digital economy target and is expected to generate over a million jobs across the value chain.
The journey is long and complex, but with the momentum generated by key investments like Tata’s ventures in Gujarat and Assam, and the unwavering commitment behind the India Semiconductor Mission, India’s silicon dreams are not just possible – they are rapidly becoming a tangible reality, poised to power the next wave of global technological advancement.
Frequently Asked Questions about India’s Semiconductor Mission:
- What is the primary goal of the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)?
The ISM’s primary goal is to build a comprehensive semiconductor and display manufacturing ecosystem in India, fostering self-reliance, attracting investments, creating jobs, and establishing India as a significant player in the global semiconductor supply chain.
- What kind of financial incentives does the Indian government offer under the ISM?
The ISM offers substantial fiscal support, including up to 50% of the project cost for setting up semiconductor fabs and display fabs, as well as capital expenditure support for ATMP units, compound semiconductor fabs, and design-linked incentives for chip design companies.
- Which major companies have announced investments in India’s semiconductor sector under the ISM?
Key investors include Tata Group (for a fab with PSMC in Gujarat and an ATMP plant in Assam), Micron Technology (for an ATMP facility in Gujarat), ISMC (for a fab in Karnataka), and a joint venture between HCL and Foxconn for another ATMP unit.
- How does India plan to address the talent gap in semiconductor manufacturing?
India is leveraging its large pool of engineering graduates and implementing specific skill development programs, academic partnerships, and initiatives like the Design Linked Incentive (DLI) scheme and “Chips to Startup” (C2S) program to train a specialized workforce for the semiconductor industry.
- What are the biggest challenges India faces in establishing a robust semiconductor industry?
Significant challenges include the high capital costs of setting up fabs, long gestation periods, ensuring reliable supplies of ultrapure water and electricity, developing a localized supply chain for specialized materials and equipment, and competing with established global semiconductor hubs.
- What is the expected economic impact of India’s semiconductor mission?
The mission is projected to significantly boost India’s digital economy, contributing towards the $1 trillion target by 2030. It’s expected to attract billions in investment, generate over a million direct and indirect jobs, and catalyze growth across sectors like automotive, telecom, and consumer electronics.
- How will the ISM strengthen India’s position in the global supply chain?
By establishing domestic manufacturing capabilities for chips and packaging, India aims to reduce import dependence, enhance supply chain resilience for critical electronics, and emerge as a reliable alternative manufacturing base for global companies looking to diversify their supply chains (a “China+1” strategy).

Leave a Reply to Tata vs. Tower: Who Will Win the Race to Modernize India's SCL Chip Lab? – 360 BIM WORLD Cancel reply